Table of contents
What is PageRank and what is it for?
PageRank (PR) is the original algorithm used by Google to rank websites in its search engine results. Thanks to this, Google is able to measure the importance of web pages and display them in its results.
It should be clarified that this is not the only algorithm used by Google, but it is the first algorithm it used and the one that served to displace all its competition.
Crowning itself as the search engine of search engines.
Why it is important
Along with Rank Brain and content quality, PageRank is one of the 3 most important ranking factors confirmed by Google.
Although Google has tried to minimize the impact of its main and most popular algorithm among SEOs and webmasters, today, more than two decades after patenting it, it is still one of the most important ranking factors.
In other words:
The links matter a lot to position a website.
Surely not in the same way as when the original algorithm was first deployed but it still influences a lot.
And that’s because PageRank:
It’s part of the Mountain View company’s great success.
How Google PageRank works
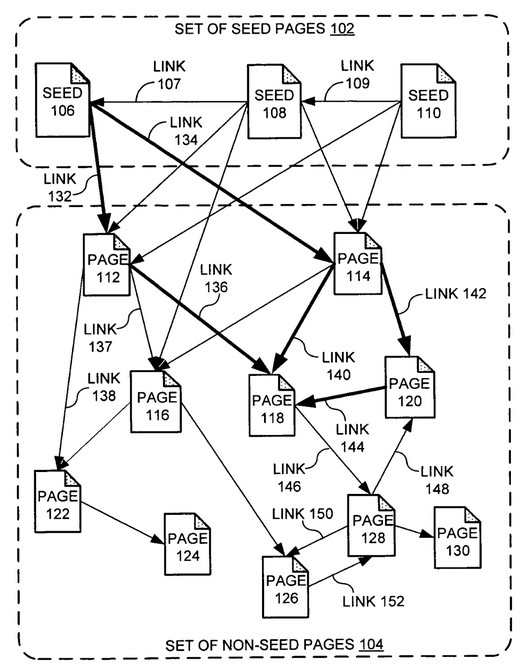
To put it very simply, PageRank works by counting the number and quality of links to a page, thus estimating the relative importance of the website in question.
The idea behind its design is to assume that more important websites receive more links.
The more links the better your website is in the eyes of Google.
Each link would act as a positive vote in a popularity contest to see who takes the top position.
However, it soon became apparent to Google that webmasters were trying to manipulate the results by using link schemes.
This obsession is one of the reasons why the search engine decided to withdraw the publication of Google PageRank, update it and reduce its weight in the algorithm.
However:
There are several known points that still influence PageRank and that you should take into account for your benefit:
1. Anchor text of the link
The anchor text of links continues to have a key weight or influence when it comes to ranking a page in the search engine results.
Google continues to use them to assign semantic context and the relationship between the linked sites and their topics.
But, at the same time, its AI takes into account or measures the naturalness of the entire link profile.
That is,
The search engine is able to identify anomalies in the use of anchor texts.
And therefore realize if they are being manipulated.
This will result in toxic and potentially dangerous links exposing you to a manual penalty or an algorithmic adjustment.
2. The probability that a link will be clicked on
Another point measured by Google is the likelihood that users will click on a link. What is known as “surfer patent” is now a key factor influencing PageRank.
But… What does it consist of?
The original PageRank algorithm assigned equal weight to links on a page.
However, the 2004 patent ensures that Google assigns a different value depending on where the links are placed.
And that is:
The probability of a footer link being clicked versus a CTA link have nothing to do with each other.
Thus, Google gives a higher relative weight to links that are highlighted or contextualized in the body of a text.
3. Internal Links or Internal PageRank Transmission
Nowadays, helping PageRank flow through your website by employing a solid internal link structure has a noticeable impact, especially when linking to pages that do not have any inbound links pointing to them.
Transmitting PageRank through internal links is a way of sending very clear signals to the search engine about which URLs or sections of your website are most relevant.
So the more website pages that point to a certain URL, the more relevant it becomes in the eyes of Google.
4. Nofollow links
NoFollow links prevented PageRank flow until recently when this became a weapon for SEOs to carve PageRank pass-through into their projects then Google decided to change their criteria.
Now Nofollow links may or may not carry over PageRank. Google no longer clarifies it but what we do know is that this type of link is relevant for positioning if they transmit quality referral traffic.
SEO implications
Understanding all of the above, what does this mean for SEOs, and how can they apply this theory to their daily work?
Here are our recommendations for improving a website’s PageRank usage:
1. Inbound Links are a Vital Ranking Factor
Nothing has managed to unseat PageRank as a reliable measure of a website’s trust and authority.
It is true that it no longer carries as much weight and that Google has managed to ignore what is considered not very “natural” links by better contextualizing anchor texts, measuring the volume of traffic referred by links, and analyzing the interaction with the site of the users of the referred traffic.
In short, it is not so much a question of volume as of quality, but inbound links are still relevant for better or worse.
2. Not all Links are the Same
The most valuable type of link you can get is one that a user is likely to click on.
A prominent link in the opening paragraph of a relevant piece of good content is infinitely more valuable than a link hidden in the footer of a website.
The same goes for the location of the link in relation to the web architecture because of the dumping factor.
A link from the home page of a website will generally be worth more PageRank than a link from a blog post.
Therefore,
Optimize the number of visually prominent links that are closer to the home page.
Internal links are gold
It’s easy to become obsessed with getting more links from external sites, but you can often gain as much or more by optimizing how link value flows through your website.
Look at your internal link structure and how PageRank can flow through your site.
Start with the web pages that have the most inbound links (often your home page and a few key pieces of popular content) and find opportunities for PageRank flow to URLs you want to increase rankings.
This will also help optimize the way Googlebot crawls your site.
4. Higher PageRank Higher Tracking Budget
So far we have talked about PageRank exclusively as a ranking factor.
But this is only one part of the picture. There is another important aspect of PageRank on domains:
It helps determine how often Googlebot crawls them.
Given the increasing amount of content, Googlebot allocates a crawl budget to each project.
And it is the PageRank that determines the frequency and time allocated to each project.
So a page with many links will be crawled more frequently than one with hardly any links relevant to the project.
5. Minimize redirections
Although it is almost impossible to avoid 100% the existence of redirects, it is advisable to ensure that most internal links point directly to the destination page.
In this way, we avoid applying the dumping factor and reduce load times by improving the crawlability of our website.
Whenever you migrate URLs keep in mind to implement single-hop redirects without chaining.
Also review pre-existing redirects, for example from previous versions of the website, and update them where possible to point directly to the final destination URL in a single-hop redirect.
In conclusion:
Remember:
PageRank is not dead.
It has undergone profound modifications and updates since its inception but it is still one of the 3 most important ranking factors in Google along with Rank Brain and content.
Its relative weight and importance in Google’s algorithm may have decreased but inbound links are still very effective in improving Google rankings.
For the moment, links are still the most powerful signal for the search engine when it comes to measuring the authority of a domain.
Therefore, PageRank will continue to be important in the future,
PageRank will still be important in 2022.
Links and recommended reading:
Frequently Asked Questions
What does PageRank mean?
The PageRank is one of Google’s most relevant algorithms for determining the position of your website in its search results. If you want to learn how to use it and the implications for your website’s ranking, you need to have a thorough understanding of how it works.
How to find out the PageRank of your page?
Google no longer makes PageRank public. However, you can use the metrics suggested by SEO services or tools to get an idea. There are the different DA indexes from MOZ, Majestic, Ahrefs or Semrush to give you an idea.
What is the PageRank score?
It is the index on a logarithmic scale that Google used to assign to each website in order to determine the authority of a website and that it stopped publishing a few years ago.
